最近在做一个课题,需要将数据建立成一棵二叉树(左右子树调换无影响那种的)。想到了强大的networkx。
在以构造图的方式建立好树后,直接使用画图代码
nx.draw(G)
plt.show()得到的结果是这样的:
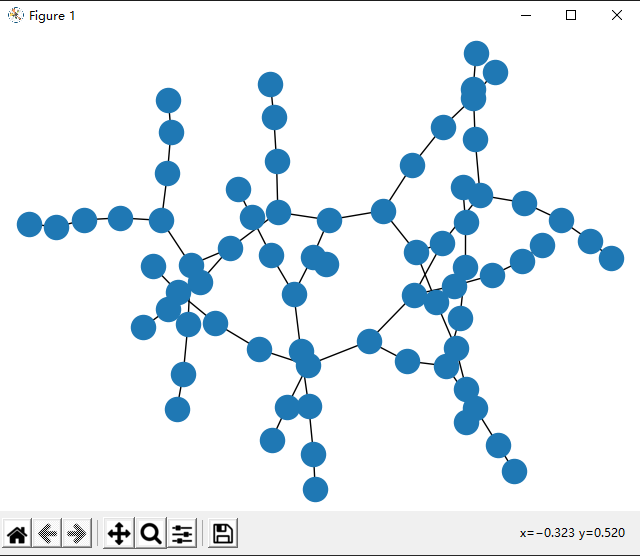
我同学说这长得像海参......
于是使用dot命令尝试生成树状图
dot_filename = str(time.time()) + '.dot'
from networkx.drawing.nx_agraph import write_dot
write_dot(G, '../dataset/pngs/' + dot_filename)
command = 'C:/"Program Files"/Graphviz/bin/dot.exe -Tpng E:/Project/dataset/pngs/' + dot_filename + \
' -o E:/WebFingerprinting/dataset/pngs/' + f.replace(".pcap", ".png")
print(command)
os.system(command)
os.remove('../dataset/pngs/' + dot_filename)这样有两个问题,一是根节点只有一棵子树时,就会掉到第二层。其次是无法显示节点属性,只能显示节点名称
找了好久,最终在stackoverflow找到了答案:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29586520/can-one-get-hierarchical-graphs-from-networkx-with-python-3/29597209#29597209
代码贴过来:
import networkx as nx
import random
def hierarchy_pos_ugly(G, root, levels=None, width=1., height=1.):
"""If there is a cycle that is reachable from root, then this will see infinite recursion.
G: the graph
root: the root node
levels: a dictionary
key: level number (starting from 0)
value: number of nodes in this level
width: horizontal space allocated for drawing
height: vertical space allocated for drawing"""
TOTAL = "total"
CURRENT = "current"
def make_levels(levels, node=root, currentLevel=0, parent=None):
"""Compute the number of nodes for each level
"""
if not currentLevel in levels:
levels[currentLevel] = {TOTAL: 0, CURRENT: 0}
levels[currentLevel][TOTAL] += 1
neighbors = G.neighbors(node)
for neighbor in neighbors:
if not neighbor == parent:
levels = make_levels(levels, neighbor, currentLevel + 1, node)
return levels
def make_pos(pos, node=root, currentLevel=0, parent=None, vert_loc=0):
dx = 1 / levels[currentLevel][TOTAL]
left = dx / 2
pos[node] = ((left + dx * levels[currentLevel][CURRENT]) * width, vert_loc)
levels[currentLevel][CURRENT] += 1
neighbors = G.neighbors(node)
for neighbor in neighbors:
if not neighbor == parent:
pos = make_pos(pos, neighbor, currentLevel + 1, node, vert_loc - vert_gap)
return pos
if levels is None:
levels = make_levels({})
else:
levels = {l: {TOTAL: levels[l], CURRENT: 0} for l in levels}
vert_gap = height / (max([l for l in levels]) + 1)
return make_pos({})
def hierarchy_pos_beautiful(G, root=None, width=1., vert_gap=0.2, vert_loc=0, xcenter=0.5):
'''
From Joel's answer at https://stackoverflow.com/a/29597209/2966723.
Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike
If the graph is a tree this will return the positions to plot this in a
hierarchical layout.
G: the graph (must be a tree)
root: the root node of current branch
- if the tree is directed and this is not given,
the root will be found and used
- if the tree is directed and this is given, then
the positions will be just for the descendants of this node.
- if the tree is undirected and not given,
then a random choice will be used.
width: horizontal space allocated for this branch - avoids overlap with other branches
vert_gap: gap between levels of hierarchy
vert_loc: vertical location of root
xcenter: horizontal location of root
'''
if not nx.is_tree(G):
raise TypeError('cannot use hierarchy_pos on a graph that is not a tree')
if root is None:
if isinstance(G, nx.DiGraph):
root = next(iter(nx.topological_sort(G))) # allows back compatibility with nx version 1.11
else:
root = random.choice(list(G.nodes))
def _hierarchy_pos(G, root, width=1., vert_gap=0.2, vert_loc=0, xcenter=0.5, pos=None, parent=None):
'''
see hierarchy_pos docstring for most arguments
pos: a dict saying where all nodes go if they have been assigned
parent: parent of this branch. - only affects it if non-directed
'''
if pos is None:
pos = {root: (xcenter, vert_loc)}
else:
pos[root] = (xcenter, vert_loc)
children = list(G.neighbors(root))
if not isinstance(G, nx.DiGraph) and parent is not None:
children.remove(parent)
if len(children) != 0:
dx = width / len(children)
nextx = xcenter - width / 2 - dx / 2
for child in children:
nextx += dx
pos = _hierarchy_pos(G, child, width=dx, vert_gap=vert_gap,
vert_loc=vert_loc - vert_gap, xcenter=nextx,
pos=pos, parent=root)
return pos
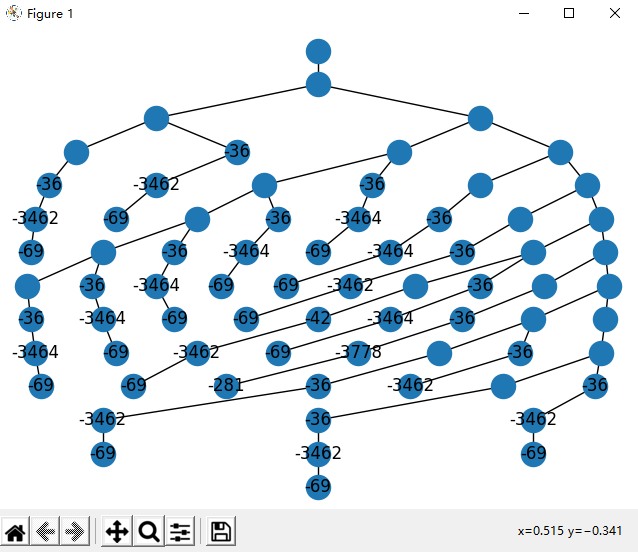
return _hierarchy_pos(G, root, width, vert_gap, vert_loc, xcenter)这里有两个函数,分别是hierarchy_pos_ugly和hierarchy_pos_beautiful,前者生成的树比较丑,但是每一行均匀分布,适合绘制大型树,后者生成的树比较美观,但是大型树会有严重重叠。
使用方法为:
pos = networkx_tree.hierarchy_pos_beautiful(G, "Root") # 生成树的节点位置信息,第二个参数为根节点名
node_labels = nx.get_node_attributes(G, 'attr') # 提取树的属性标签,第二个参数为属性标签名
nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True, labels=node_labels) # 绘制树
plt.show() # 显示两者效果图如下:
ugly:
beautiful:
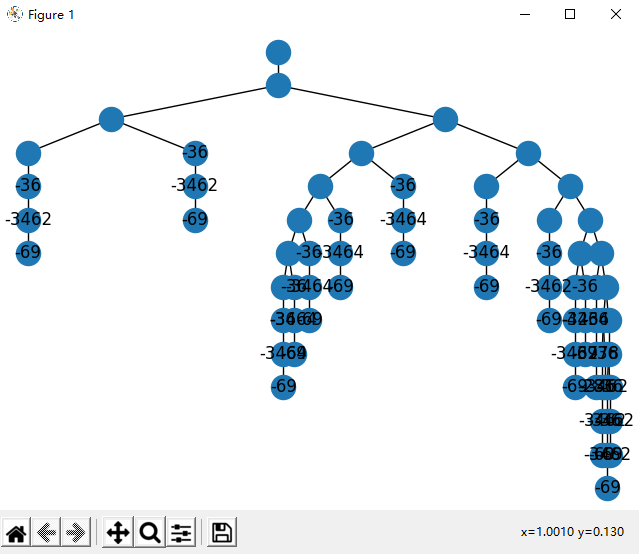


手动狗头(
楼主这布局有点丑,建议自己写个简单算法布局or使用igraph.layout的自动布局
你上面的搜索框用不成
alert(“哈哈”)
你的搜索框功能还没写?